


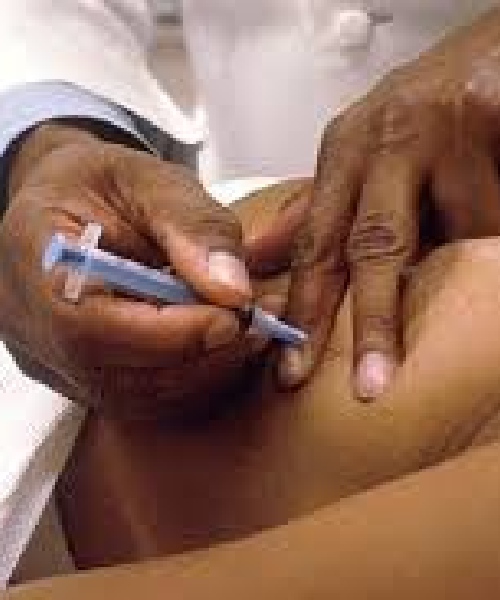
Fine-needle aspiration: What is fine-needle aspiration?
In most cases, a fine needle aspiration is chosen when the lump is likely to be filled with fluid. If the lump is easily accessible or if the doctor suspects that it may be a fluid-filled cystic lump, the doctor may choose to conduct a fine-needle aspiration (FNA). During this procedure, the lump should collapse once the fluid inside has been drawn and discarded. Sometimes, an ultrasound is used to help your doctor guide the needle to the exact site,
whereby sound waves create a picture of the inside of the breast. If the lump persists, the surgeon or radiologist, a doctor who specializes in medical imaging such as x-rays and mammograms, will perform a fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNABx), a similar procedure using the needle to obtain cells from the lump for examination.
Core needle biopsy :- What is a core-needle biopsy?
Core needle biopsy is the procedure to remove a small amount of suspicious tissue from the breast with a larger “core” (meaning “hollow”) needle. It is usually performed while the patient is under local anesthesia, meaning the breast is numbed. During the procedure, the doctor may insert a very small marker inside the breast to mark the location of the biopsy. If surgery is later required, the marker makes it easier for the surgeon to locate the
abnormal area. Even if no further treatment such as surgery is needed, the marker allows a breast imaging radiologist to see on future mammograms where the biopsy was done. The radiologist or surgeon performing the core-needle biopsy may use specialized imaging
equipment to guide the needle to the desired site. As with fine-needle aspiration, this may involve ultrasound.
During an ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy, the patient lies down while the doctor holds the ultrasound against the breast to direct the needle. On the other hand, during a stereotactic-guided core-needle biopsy, the doctor uses x-ray equipment and a computer
to guide the needle. Typically, the patient is positioned lying on the stomach on a special table that has an opening for the breast, and the breast is compressed, similar to a mammogram. Occasionally, no imaging equipment is used, but this is typically only in cases where the lump can be felt through the skin. This type of procedure is called a freehand core-needle biopsy. There are fewer side effects associated with a core-needle biopsy than with surgical biopsy.

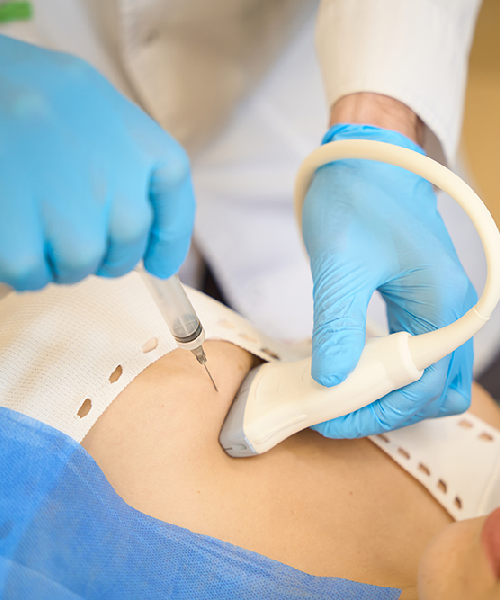
Surgical biopsy:- What is a surgical biopsy?
(Also known as “wide local excision,” “wide local surgical biopsy,” “open biopsy,” or “lumpectomy”)
As with a core-needle biopsy, a surgical biopsy is done while the patient is under local anesthesia, or general anesthesia in some cases. Typically, this test is performed in a hospital setting where an IV and medications are administered to make the patient drowsy. The surgeon makes a one- to two-inch cut on the breast and then removes all or part of the
abnormal lump and often a small amount of normal-looking tissue, known as the “margin.” If the lump cannot be easily felt but can be seen on a mammogram or ultrasound, a radiologist may insert a thin wire to mark the suspicious spot prior to the surgeon performing the biopsy. Once again, a marker is usually placed internally at the biopsy site at the conclusion of the procedure.
Scarless removal of breast lump: An introduction to VABB
Through the course of life, a woman’s body undergoes several changes. While some changes are natural, others can be unexpected and anxiety-inducing such as breast lumps. If you feel a lump in your breasts, the first thought that you are likely to have is that of breast
cancer. While breast cancer is the most common cancer in India accounting for nearly 14% prevalence, it is not the only disease leading to lumps. Benign (non-cancerous) breast lumps are also highly common. However, benign or malignant, scarless removal of breast
lump is possible. A breast lump is a localised growth of tissue within the breast. These tissues may or may
not be cancerous. When a woman experiences this atypical growth, she, expectedly, have upheavals of
emotions including fear, worry and panic. The next thought in line follows the breast lump removal that again causes distress. It is because according to popular opinion, a breast lump removal surgery leaves a lasting scar that can impact your self-image. Nonetheless, advances in medical science have evolved and introduced a new technology for scarless removal of breast lump – Vaccum Assisted Breast Biopsy
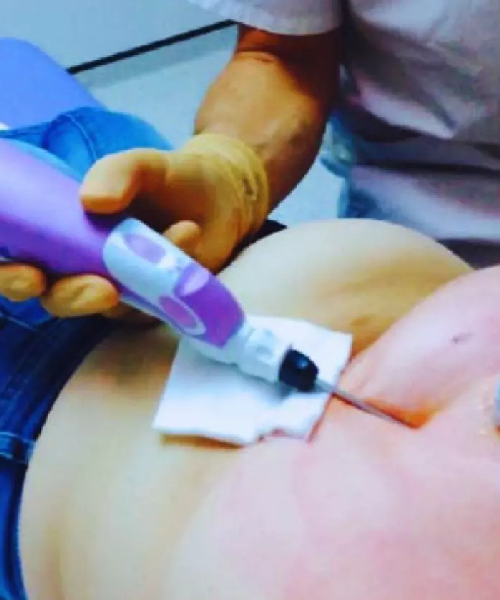
What are vacuum assisted breast biopsy indications?
A breast biopsy is indicated when a patient displays symptoms of breast abnormality or when she undergoes her routine screening based on her risk factors of the concerned disease. However, an open breast biopsy is not considered a highly preferable option among patients as it causes an altered appearance of your breast which can be a distressing experience. As vacuum assisted breast biopsy is a scarless breast surgery intervention. VABB is indicated for both diagnostic and therapeutic reasons.
